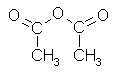
Acetic anhydride
| 원료 | |||||||||||||
| 생산물 | acetic anhydride | ||||||||||||
| 적용 | Production of acetic anhydride from methanol and carbon monoxide by carbonylation of methyl acetate. | ||||||||||||
| 설명 | Description: Methyl acetate is carbonylated with carbon monoxide to form acetic anhydride at very high yields in the presence of a homogeneous, multicomponent catalyst system. Moderate conditions of temperture and pressure are used for the reaction: A novel and efficient system that combines reaction and distillation has been developed to produce methyl acetate at essentially quantitative yields. If recycle acetic acid is available, e.g., from cellulose acetate production, it is used directly to esterify methanol at mild conditions. Methyl acetate is recovered at high purity while the water of esterification is removed from the system. If no recycle acid is available, or if the quantity is insufficient, then a portion of the acetic anhydride is used to provide the methyl acetate needed. Thus no external source of acetic acid is needed. Effluent from the carbonylation reactor is reduced in pressure and separated by distillation to yield a high-purity acetic anhydride product. Yields: The yield of methyl acetate from methanol and acetic acid (or acetic anhydride) is over 99.9% of theoretical. The overall yield from methanol to product acetic anhydride is above 95 mol%. Economics: Production costs for acetic anhydride by the carbonylation route are significantly lower than for the older route based on ketene, particularly with regard to utilities. |
||||||||||||
| Properties in KDB |
Component Names and Formula
Click here to find more informations from KDB.
|