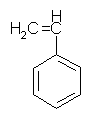
Styrene
| 원료 | Benzene; Ethylene | ||||||||||||
| 생산물 | styrene | ||||||||||||
| 적용 | To produce polymer-grade styrene monomer by alkylating benzene with ethylene to form ethylbenzene, which is dehydrogenated to styrene. | ||||||||||||
| 설명 | Description: The alkylation, with benzene in excess from the benzene drying column (1), takes place in a homogeneous system (2) using aluminum chloride catalyst. Catalyst is continuously removed (3) and replenished. Removed catalyst is converted to aqueous aluminum chloride solution as a byproduct suitable for water treatment applications. A fractionation system (4,5,6) recovers high purity ethylbenzene. Polyethylbenzenes and unconverted benzene are recycled. The heavy residue, flux oil, is used for fuel oil. Ethylbenzene dehydrogenation (7) also is catalytic, using commercially available catalyst with about two years' life. An innovative reactor design provides high thermal efficiency and excellent mechanical reliability. Process condensate from the dehydrogenations step is stripped (8) to remove dissolved aromatics and is used inside the unit as boiler feed water. A fractionation train (9,10) separates high-purity styrene, unconverted ethylbenzene, and the relatively minor reaction byproducts. Toluene is produced as a minor byproduct (11,12).
Operating conditions: The alkylation step operates efficiently at low benzene-to-ethylene ratios, resulting in low associated processing costs. Heat of reaction recovered as steam that can be internally utilized. Operating data: Feed, kg/kg monomer
Note: Feed and utility requirements presented are representative; they would be optimized for specific raw material and utility availability and cost conditions. This includes the most up-to-date commercially proven and patented system for recovering about 500 kcal low-level energy per kg of styrene produced, without requiring any compression equipment. |
||||||||||||
| Properties in KDB |
Component Names and Formula
Click here to find more informations from KDB.
|